
8 Signs of Eye Trauma
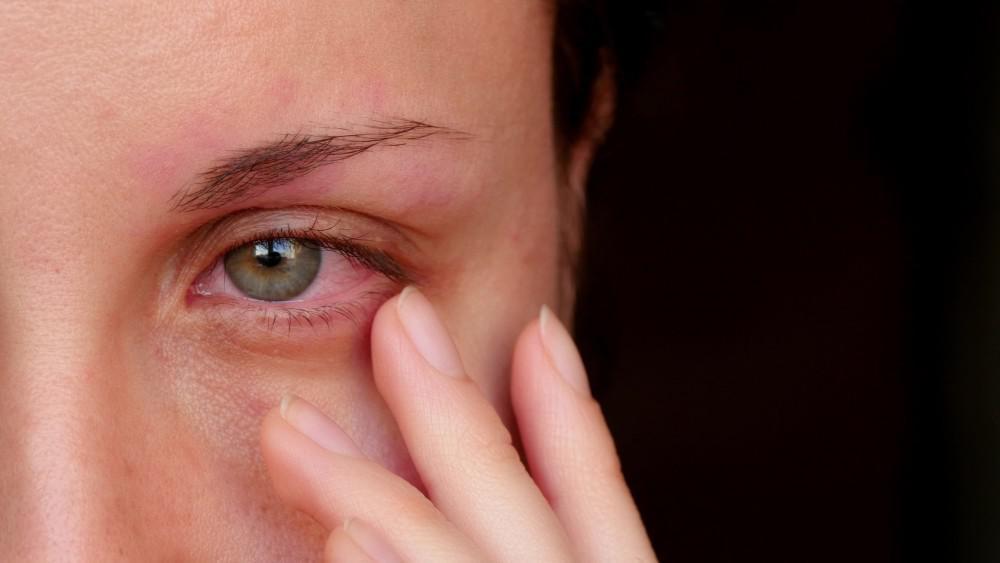

More than 2.4 million Americans injure their eyes every year, and up to 20% of eye injuries result in temporary or permanent vision loss. Most eye traumas are work-related or involve chemicals, although eye injuries are also common in sports, automobile accidents, and personal assault.
If you sustain an eye trauma, our team of expert ophthalmologists at the Retina Specialists offices — in Dallas, DeSoto, Plano, Mesquite, and Waxahachie, Texas — offer expert treatment to protect your vision. Our team shares eight of the common signs of eye trauma, so you know when to seek immediate help.
1. Eye pain
You should never ignore pain, especially if your eye has suffered trauma. It’s how your body signals that there’s a problem. If your eye hurts, whether it’s burning or throbbing, if your pain persists for more than a minute or two, you need to call our team of ophthalmologists for help.
2. Blurry vision
Blurry vision is another common sign of an eye problem. While blurry vision is often due to insufficient lubrication in your eye, sudden or severe blurriness can indicate a problem with your optic nerve that may occur after trauma. A problem like closed-angle glaucoma can also cause sudden eye pain and blurred vision, and it’s a common cause of blindness.
3. Burning feeling
If any kind of foreign substance was splashed into your eye and it burns, find the nearest eye washing station or rinse your eye with clean, warm water at a sink for 20 minutes. If you’re at home, using a shower may work better. Then come in to see us for a professional evaluation and treatment, if needed.
4. Redness
Your eyes might become red if the air is very dry or smokey. Redness can also be caused by infections like conjunctivitis (aka pink eye). Severely red eyes can be caused by broken blood vessels in your eye, which may be caused by trauma. Redness may subside on its own, but if it’s persistent or accompanied by pain, you’re best off consulting with one of our trusted eye doctors.
5. Double vision
Double vision can be a sign of a neurological problem, which may or may not result from trauma. If you close one eye and your double vision stops, have a friend or family member take you to the emergency room. It would be best if you still talked to your ophthalmologist about double vision, as dry eyes and cataracts can also cause it.
6. Droopy eyelid
While age-related collagen and elastin loss makes everyone’s facial skin a little limp, a sudden and severe droop in one of your eyelids is a sign of a stroke or a neurological problem such as Bell’s Palsy or nerve damage. While this isn’t an actual eye trauma, it’s important enough to mention in this list.
7. Abnormal pupils
Your pupils should be approximately the same size. They open and close, depending on the amount of light in your environment. Different-sized pupils may be a sign of eye trauma or may indicate a health emergency, like a stroke or aneurysm.
8. A sudden increase in floaters
Almost everyone has a floater in their vision every now and then. However, a sudden increase in floaters — it might look like a shower of them — is a warning sign of a retinal tear. Seeing stars or flashes of light along with increased floaters is another warning sign of this traumatic eye problem.
Fortunately, you can call one of our offices for immediate specialist eye care when you notice any of these symptoms. Our team of ophthalmologists provides outstanding exams and tests to evaluate your condition and identify the best treatment to preserve your vision.
You Might Also Enjoy...


How Aging Impacts Retinal Health
Vitrectomy: The Outpatient Surgery That Can Save Your Vision

When to Seek Treatment for Eye Trauma

What Happens During a Diabetic Eye Exam?


